Sapropterin therapy: sapropterin is a synthetic form of cofactor BH4 and is able to partially restore PAH activity or supply BH4, thereby decreasing the amounts of phenylalanine and phenylketone and increasing tyrosine (and dopamine) production
What Decreases BH4?
Mechanism Of Action
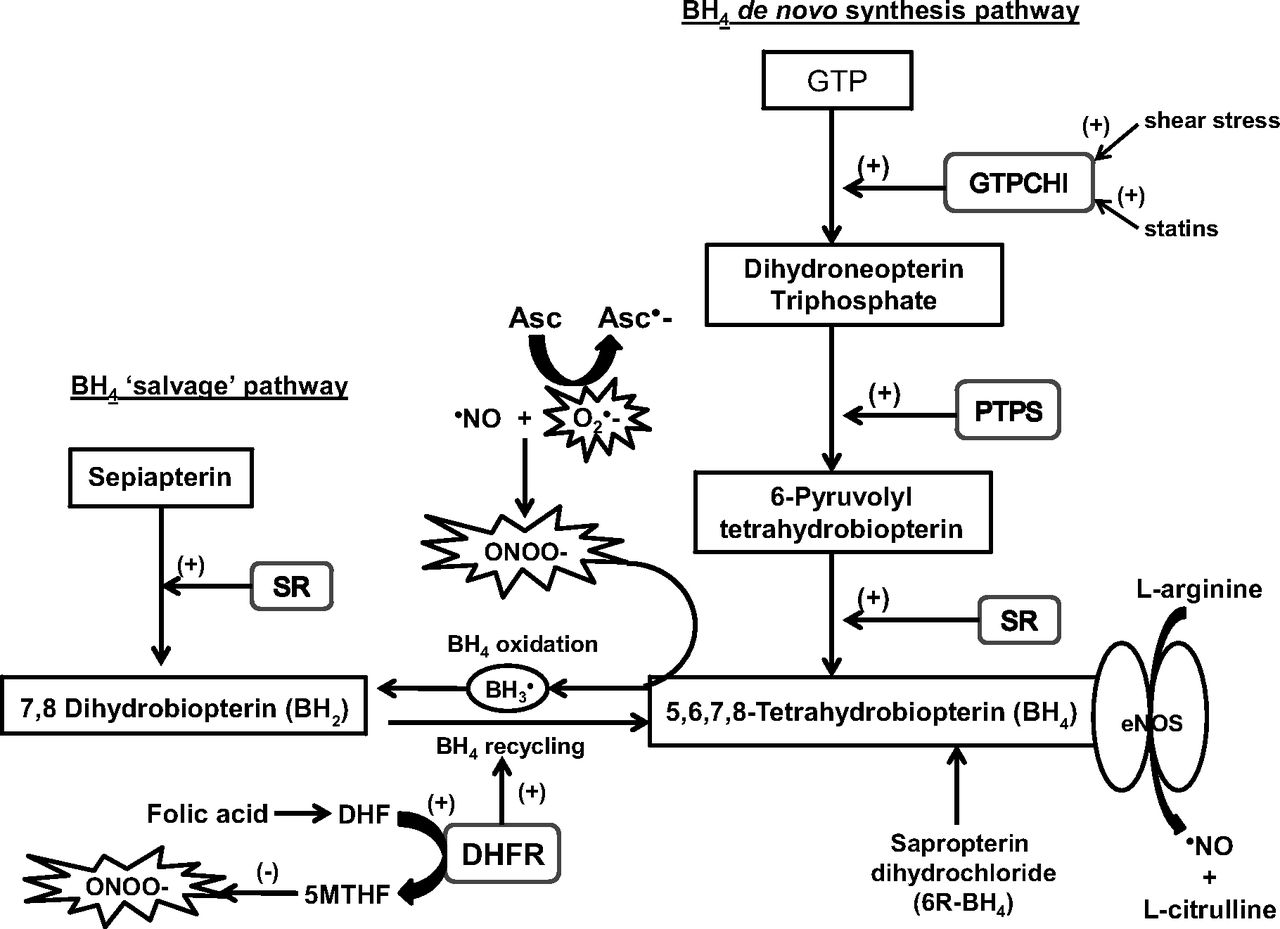
Intracellular 5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4), synthesis, oxidation, and recycling in endothelial cells. GTP, guanidine triphosphate; GTPCHI, GTP cyclohydrolase I; PTPS, pyruvoyl tetrahydrobiopterin synthase; SR, sepiapterin reductase; DHFR, dihydrofolate reductase; ˙NO, nitric oxide; O2·−, superoxide anion radical; ONOO−, peroxynitrite; H202, hydrogen peroxide; BH3˙, trihydrobiopterin radical; DHF, dihydrofolate; 5MTHF, 5-methyltetrahydofolate; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; Asc, ascorbate; Asc˙−, ascorbate radical.
Here is a summary of the BH4-related biochemical transformations: R
- Phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) enzyme to convert Phenylalanine (PHE) to Tyrosine (TYR)
- Tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) enzyme to convert Tyrosine to L-DOPA (DOPA)
- Tryptophan hydroxylase (TPH) enzyme to convert Tryptophan to 5-Hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP)
- Nitric oxide synthase (NOS) enzyme to convert a Arginine (ARG) to Nitric oxide (NO)
The enzyme DHFR may recycle BH2 into BH4.
This would be after exogenously administered BH4 has been oxidized into BH2. R
Nitric Oxide Production
BH4 is important for nitric oxide synthases and when it is missing, enzymes become "uncoupled". This uncoupling produces Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) rather than NO.
Genetics For Low BH4
Defects in these genes can predispose you to low BH4 production.
- MTHFR A1298C (rs1801131) is involved in converting 5-methylfolate (5MTHF) to tetrahydrofolate (THF). A1298C helps generate BH4. R
- CBS catalyzes the first step of the transsulfuration pathway, from homocysteine to cystathionine. BH4 can also become depleted with a CBS upregulation. R
- DHFR encodes an enzyme that plays a part in folate metabolism. R R
- GCH1 encodes an enzyme called GTP cyclohydrolase 1. It helps produce BH4. R
- SPR provides instructions for making the sepiapterin reductase enzyme, which is involved in the last of three steps of producing BH4. R
- GCHFR binds to and mediates tetrahydrobiopterin inhibition of GTP cyclohydrolase I. R
- PTS facilitates folate biosynthesis. A mutation in this gene could directly cause BH4 deficiency. R
- QDPR produces the enzyme quinoid dihydropteridine reductase. This enzyme is part of the pathway that recycles BH4. R
Biosynthesis For Low BH4

GTP (guanosine triphosphate) converts into dihydroneopterin tiphosphate (GCH1 gene).
Dihydroneopterin triphosphate and magnesium convert into 6-pyruvoyl-tetrahydropterin vita (PTS gene).
Dihydroneopterin triphosphate can degrade into neopterin.
6-pyruvoyl-tetrahydropterin and NADPH convert into BH4 and NADP (SPR gene).
6-pyruvoyl-tetrahydropterin can also degrade to sepiapterin and then BH2.
BH2 and folate convert to BH4 (DHFR gene).
GCHFR can be a feedback mechanism for GCH1 activity.
GCHFR will inhibit GCH1, but if phenylalanine is present, it will stimulate GCH1.
- Increase BH4
- Exercise R
- Far-Infrared R
- Fenofibrate R
- Folate/Methylfolate is a potent peroxynitrite scavenger R
- Losartan R
- Nitrites R R
- Royal Jelly
- SAM-e
- Statins/HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors R R
- Vitamin C R R
Ways To Increase Tyrosine Hydroxylase
My Top 5 Ways To Increase TH
- Bright Light Device (or I'll use Sunlight and Blue Light)
- Butyrate R
- Exercise R
- Music - this is what I listen to R
- Uridine + Eating Fish (or fish oil) R
Diet / Lifestyle / Devices:
- Avoid Chronic Stress R
- Black Pepper R
- Bright Light (increases TH in eye and hypothalamus, but decreases TH-neurons) R R R
- Caffeinated Teas (Green, Black, or Oolong) and Coffee (Super Coffee would stabilize TH) R R
- Caloric Restriction (increases in substantia nigra, but reduces it in striatal area) R R
- Chronic Hypoxia R
- Cold Exposure (showers, baths, gear) R
- Electroshock Therapy R
- Enriched Environments R
- Exercise R R
- Fish Oil or Krill Oil (specifically DHA) R R
- Garlic R
- High Protein Diet (specifically high in Tyrosine) R
- Music (possibly) R
- Nerve Stimulation (use Nervana) R
- Photobiomodulation (infrared LLLT) R
- Spirulina R R
Supplements:
- An-Jun-Ning R
- Bacopa R
- Baicalein/Skullcap (protects TH neurons from oxidative-stress induced death) R
- Beta-caryophyllene R
- Bupleurum + Angelica (Dong Qui) + Paeonia suffruticosa R
- Butyrate R
- Caffeine R
- Cistanche R
- Copper (low) R
- Cordyceps R
- Creatine R R
- Da Bu Yin Wan R
- Eucommia ulmoides (Du Zhong) R
- Ferulic Acid (in striatum) R
- Forskolin R
- Gastrodin R R R
- Geng Nian (Tian Gui aka Menoplease) R
- Ginkgo Biloba (increases TH neurons) R
- Hepad (strong - combo of Cang Zhu, Cnidium, Paeonia japonica, Fu Ling, Gastrodin, and Jujube) R
- Horny Goat Weed (Icaarin) R
- Inositol R
- Iron (low) R
- Jiaogulan (Gynostemma protects TH neurons from oxidative-stress induced death) R
- Licorice (stabilizes TH during stress) R
- Lion's Mane (prevents TH reduction from oxidative stress, but doesn't increase TH) R
- Lithium (increases TH in brain but reduces it in adrenals) R R
- Milk Thistle (prevents TH reduction from oxidative stress, but doesn't increase TH) R
- Mucuna pruriens + Ashwaganda (they work on TH independently, but the combo is stronger) R R R R
- Mulberry (prevents TH reduction from oxidative stress, but doesn't increase TH) R
- N-acetylcysteine (NAC - strong) R
- Narigenin R
- Nobiletin R
- Olive Leaf Extract (protective of TH neurons) R
- Quercetin R
- Retinol (strong) R
- Rhodiola (salidrosides balance TH levels, whereas tyrosol decreases TH, see below) R
- Safflower R
- Selenium (low doses) R
- Stephania (tetrandra) R
- Tangerine (Rikkunshito) R
- Tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA) R
- Thunder God Vine (Triptolide protects TH neurons from neuroinflammation) R R
- Toki To (TKT) R
- Uridine R
- Vitamin B6 (P5P) R
- Vitamin C R
- Xiao Yao San R
- Yin Yang Huo R
Hormones:
- Insulin R
- Melatonin (increases it in ventral mesencephalon but not in the hypothalamus) R R
- Oxytocin (coexpressed in the hypothalamus) R
- Vitamin D (D3) R R R
Drugs/Chemicals:
- Alcohol (acutely and decreases with alcohol tolerance) R R
- Amphetamines R
- BH4 (tetrahydrobiopterin) R
- Bradykinin R
- Bromantane (Lodastan) R R R
- Carbachol R
- Ceftriaxone R
- Cilostazol R
- Cocaine (decreases w/ tolerance) R
- Deferoxamine R R
- Dexamethasone R
- Fluoxetine R R
- Hydrocortisone R
- Intranasal Testosterone Propionate R
- Nicotine R
- Nomifensine R
- Perindopril R
Pathways:
- Acetylcholine R
- α-Synuclein inhibition R
- BDNF R R
- cAMP (PKA) R R
- CB1 (increases TH activity) R
- CB2 (protects TH neurons) R
- CDNF R R
- EGF R
- ERK R
- FoxO1 inhibition (activation lowers activity) R
- GDNF (dose dependent) R
- HIF1alpha R
- Hsc70 R
- Increase Tregs cells R
- Laminin R
- MANF R
- M1 mAChR R
- nAChR R
- NGF R R
- Nitric Oxide R
- Noggin R
- NRF2 (protective of TH neurons) R
- NR4A2 (downstream increases TH, VMAT2, and DAT) R
- PARK7/DJ-1 R
- PDE2 inhibition R
- PPAR-γ R
- ser40 R
- TGF-B1 R
Other:
What Reduces Tyrosine Hydroxylase?
Lifestyle:
Devices:
- Deep Brain Stimulation (reduced activity in the PFC) R
Supplements:
- Acetyl-L-Carnitine (ALCAR) R
- Ginger R
- Ginseng R R
- Glutamine R
- Glutathione (in cancer) R
- Manganese R
- Nicotinamide (may increase TH in adrenals) R R
- Pine Bark R
- Propolis R
- Rhodiola (tyrosol, not salidroside, inhibits tyrosinase thus inhibiting melanin production) R
- SAMe R
- Selenium (chronic high doses) R
- Theanine R

